Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
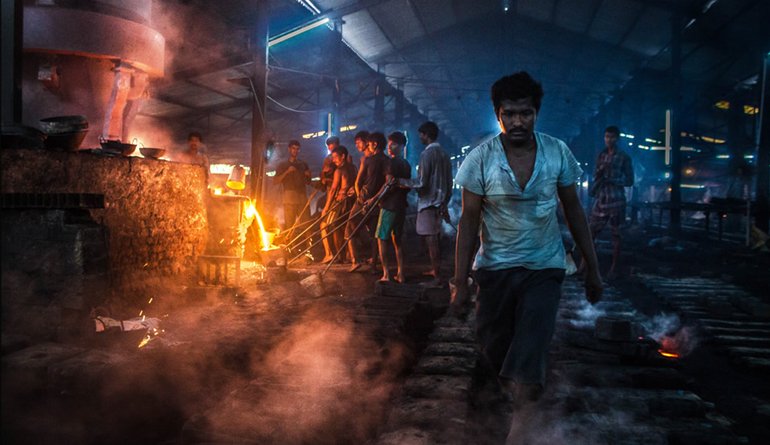
C.I. Casting
CI Casting, also known as Cast Iron Casting, is a metal casting process that involves pouring molten iron into a mold to create various products. Cast iron is a group of iron-carbon alloys with a carbon content greater than 2%. It is known for its excellent castability, high strength, and wear resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
The CI Casting process begins with the melting of iron, typically in a blast furnace. The molten iron is then poured into a mold, which can be made of sand, ceramic, or metal. The mold is designed to have the desired shape and dimensions of the final product. Once the molten iron is poured into the mold, it is left to cool and solidify. After solidification, the mold is removed, and the cast iron product is ready for further processing or use.
There are different types of cast iron used in CI Casting, including gray iron, ductile iron, white iron, and malleable iron. Each type has its own unique properties and applications. Gray iron, for example, is known for its excellent damping capacity and is commonly used in automotive components and machinery parts. Ductile iron, on the other hand, has high tensile strength and is often used in pipes and fittings.
CI Casting offers several advantages over other casting methods. It allows for the production of complex shapes with high accuracy and repeatability. It also provides excellent thermal conductivity and is resistant to deformation at high temperatures. Additionally, cast iron products have good machinability, allowing for easy post-processing.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the CI Casting process and explore the various stages involved.



